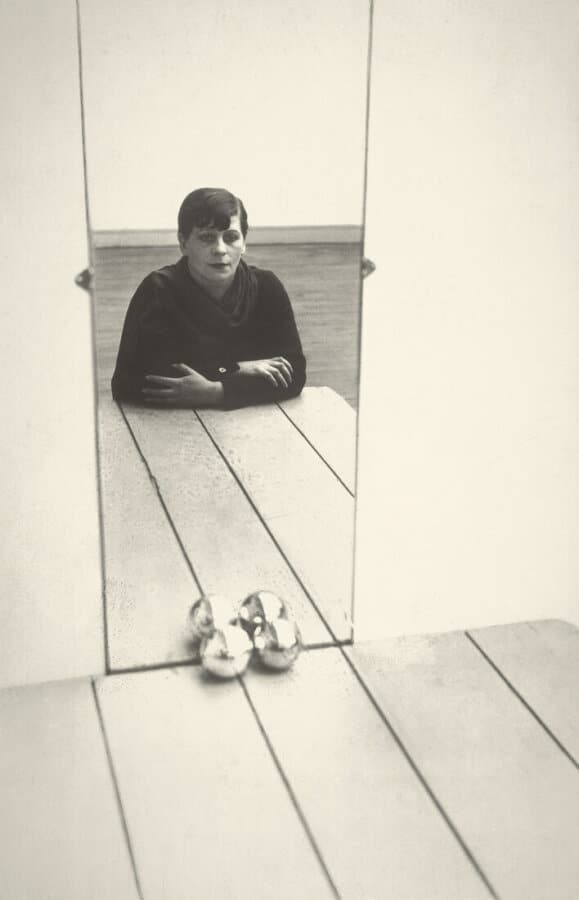
Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Kunstbibliothek. Florence Henri © Galleria Martini & Ronchetti
Exhibition
Florence Henri
Mirror of the avant-garde 1927-1940
From 24 February to 17 May 2015
Jeu de Paume – Paris
To watch the video portrait:
Florence Henri (New York 1893 – Compiègne (France) 1982) was a multi-faceted artist, who was first known for her paintings before making a name for herself as a major figure in avant-garde photography between the end of the 1920s and the beginning of the 1940s. She lived in Silesia, Munich, Vienna, Rome and above all Berlin, before finally settling in Paris in 1924 and devoting herself to photography. This medium enabled her to experiment new relationships with space, in particular by the use of mirrors and other objects in her compositions.
The Jeu de Paume is presenting a vast panorama of Florence Henri’s photographic production from 1927 to 1940, including her self-portraits, abstract compositions, portraits of artists, nudes, photomontages, photocollages, as well as documentary photos taken in Rome, Paris and Brittany. The exhibition comprises vintage prints, various documents and published material.
When she was young, Florence Henri studied music and painting in England and Germany. In 1919, when she was a student at the Berlin Academy of Arts, she made the acquaintance of writer and art historian Carl Einstein and became friends with several figures of the avant-garde, including Hans Arp, Adrian Ludwig Richter, John Heartfield and Lázló Moholy-Nagy. She took classes with Paul Klee and Vassily Kandinsky at the Bauhaus in Weimar. In 1924 she moved to Paris, where she followed classes at the Académie Montparnasse, whose director was André Lhote, then at the Académie moderne (founded by Fernand Léger and Amédée Ozenfant). In 1927, after a visit to Bauhaus in Dessau, she abandoned painting in favour of photography. It was at this time that she produced her famous self-portraits in mirrors and her still lifes; the result of her first steps in the spatial research that she would carry out through the medium of photography.
Between the end of the 1920s and the beginning of the 1930s, three mythical exhibitions in terms of the history of European photography took place in Germany: “Fotografie der Gegenwart” at the Folkwang Museum in Essen (1929); “Film ind Foto” (Fifo) organised the same year by the Deutscher Werkbund in Stuttgart and “Das Lichtbild” held in Munich (1931). These exhibitions bore witness to the rapid expansion of new photographic concepts and a rupture with tradition. Fifo marked the zenith of the Neues Sehen (New Vision) movement of which László Moholy-Nagy was an exponent and “Das Lichtbild” marked the triumph of Neue Sachlichkeit (New Objectivity), whose leading representative was Albert Renger-Patzsch.
Florence Henri was invited to show an important number of prints at these three exhibitions in recognition of her photographic production during this fundamental period that saw the photography used to free our vision and open out onto new experiences.
Florence Henri’s studio rivalled that of Man Ray, even if she had also opened a school of photography where Lisette Model and Gisèle Freund, amongst others, would enrol. In fact, despite the central position that her oeuvre occupied in avant-garde photography at the end of the 1920s, her reputation as a portraitist in Paris, and the fact that her photos had been published in many of the period’s illustrated magazines such as Arts et Métiers and Lilliput etc, Florence Henri’s body of work remains largely unknown.
László Moholy-Nagy’s* comments are a perfect illustration of Florence Henri’s position: “With Florence Henri’s photos, photographic practice enters a new phase, the scope of which would have been unimaginable before today. Above and beyond the precise and exact documentary composition of these highly defined photos, research into the effects of light is tackled not only through abstract photograms, but also in photos of real-life subjects. The entire problem of manual painting is taken onboard by the photographic process and is manifestly given a whole new depth thanks to this new optical instrument. Reflections and spatial relationships, superposition and intersections are just some of the areas explored from a totally new perspective and viewpoint.”
*László Moholy-Nagy, “Zu den Fotografien von Florence Henri”, i10, No 17-18, Amsterdam, December 20, 1928.
Curator: Cristina Zelich, independent curator.
Exhibition organized by Jeu de Paume, with the kind collaboration of the Florence Henri Archive, Genoa.
Media partners: A NOUS PARIS, De l’air, Stylist, Time Out Paris, TSF Jazz.
Acknowledgements to the hôtel Castille, Paris